The osteochondrosis of the spine is a chronic disease in which they occur degenerative changes of the vertebrae and are located between them the intervertebral discs. Depending on the site of the defeat of the spine are distinguishable: the osteochondrosis of cervical, the osteochondrosis of breastfeeding and of the division and the osteochondrosis back. For the diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the spine, it is necessary to perform an x-ray, and in the case of complications (for example, a herniated intervertebral disk) - magnetic resonance imaging of the spine. In the treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine, along with medicated methods are widely applied, reflexology, massage, quiroprctica, physical therapy and curative physical education.
The etiology and pathogenesis of the
To a greater or lesser extent, the osteochondrosis of the spine develops to all of the old people and is one of the aging processes of the body. Sooner or later in intervertebral disc arise atrophic changes, however, the injuries, illnesses, and different overload of the vertebral column contribute more to the early onset of osteochondrosis. Most commonly found in the osteochondrosis of cervical and osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
Developed around 10 theories of osteochondrosis: vascular, hormonal, manual, hereditary, infectious-allergic and other. But none of them gives a full explanation will occur in the backbone of the changes, but are complementary.
It is considered that the fundamental aspect in the emergence of the degenerative disc disease is the constant overload on vertebral segment, which consists of two adjacent vertebrae. This loading may occur as a result of the stereotype — the individual posture the way you sit and walk. The violation of posture, the seat in a bad posture, walking with problems of the spinal column cause an additional load on the disks, ligaments and muscles of the spine. A process that can be aggravated due to the nature of the structure of the vertebral column and of the failure of trophic its tissues, derived from hereditary factors. Most often, defects in the structure are found in the cervical region and result in veins to the violations and to the early appearance of the signs of degenerative disc disease, cervical spine.
The emergence of the degenerative disc disease lumbar of most related with your overhead when slopes and gradients of severity. Healthy intervertebral the unit can withstand large loads thanks to the hydrophilicity located in the centre of the city pulpous nucleus. The nucleus contains a large amount of water, and the liquid, as is known, little is compressed. The gap of a healthy intervertebral disc can occur when the force sdavleniya of more than 500 kg, while modified as a result of the degenerative disc disease, the disc is broken, when the force sdavleniya of 200 kg of Load of 200 kg experiences a lumbar spine of a person weighing 70 kg, when kept at 15 kg load in the position of inclination of the trunk forward in the 200. It is a great pressure, due to the small magnitude of the pulpous nucleus. By increasing the inclination of up to 700 of load on the intervertebral discs m? s will be 489 kg therefore, often the first clinical manifestation of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine occur during or after lifting weights, doing the work in the home, remove the weeds from the garden, etc
The destruction of the fibrous connective tissue rings of the disc, the ligaments and the capsules of facet joints causes a reaction of the immune system and the development of aseptic inflammation with swelling of facet joints and the tissues. Due to the inclination of the vertebral bodies produces a strain of capsules, facet joints, and modified the intervertebral disc is not as firmly fixed to the body of adjacent vertebrae. It generates instability in the spinal segment. Due to the instability of possible violations of loin spinnomozgovogo a nerve with the development of the radicular syndrome. The osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, this often occurs during turning of the head, osteochondrosis back of the division — at the time of tilting the torso. It is possible the formation of the functional unit vertebral segment. It is also a result of compensation of the reduction of the vertebrate muscles.
A herniated disk is when the disk moves rearward, it causes the rupture of the posterior longitudinal ligament and bulging of the disc in the spinal canal. If the medullary canal is extruded as the core of the unit, the hernia is called the explosion. The intensity and duration of the pains of this hernia much notla explosion. The disc herniation can cause radicular syndrome or sdavleniya of the spinal cord.
The osteochondrosis occurs the proliferation of bone tissue, with education osteophytes — bony outgrowths on the bodies and the spindles of the vertebrae. Osteophytes can also cause compression of the spinal cord, or be the cause of the development of radicular syndrome.
The symptoms of osteochondrosis of the spine
The main symptom of osteochondrosis of the spine is the pain. The pain can be acute with high intensity, she looks more slight movement in the affected segment and, therefore, forces the patient to take to force the situation. Thus, while the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the patient keeps the head in the least painful position and may not rotate to the osteochondrosis of breastfeeding and of the division of pain intensifies, even with the deep breathing, and osteochondrosis of the lumbar part of the patient is difficult to sit, stand and walk. This syndrome of pain characteristic sdavleniya loin spinnomozgovogo of the nerve.
Approximately 80% of the cases it is observed a dull pain constant in nature and of moderate intensity. In these cases, during the medical examination should be differentiated from the manifestation of the osteochondrosis of the spine, of myositis the muscles of the back. A dull, aching pain on the osteochondrosis caused by excess muscle tension, retention, surprised as the engine in the segment, inflammatory or significant change of the extension of the intervertebral disc. Patients with this armbar syndrome of forcing the position of the lack, but it reveals the limitation of movements and physical activity. Patients with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, avoiding sharp turns and the tilt of the head, with osteochondrosis lumbar - slowly sit down and stand up, to prevent the inclination of the trunk.
The complications of osteochondrosis of the spine
The complications of degenerative disc disease are related to intervertebral disk herniation. To them carry compression of the spinal cord, characterized numbness, weakness of certain muscle groups of the limbs (depending on the level of sdavleniya), which leads to the appearance of paresis muscle atrophy, the change of suhozhilnih reflexes, disorders of urination and defecation. Intervertebral hernia can be the cause of the sdavleniya of the artery that feeds the spinal cord, with the education disease of the plots (infarction of the spinal cord) with the death of the nerve cells. This is manifested by the appearance of neurological deficit (violation of movements, loss of sensation, trophic disorders), corresponds to a level and the prevalence of ischemia.
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the spine
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the spine performed by a neurologist or spine. In the initial phase of producing x-rays of the spine in 2 projections. If necessary, you can make the photograph individual spinal segment and the photo with more projections. For the diagnosis of intervertebral hernia, the evaluation of the state of the spinal cord, and the detection of complications of osteochondrosis using magnetic resonance imaging (mri of the spine). It plays a great role of magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spine: tuberculous spondylitis, osteomyelitis, tumors, disease behtereva, rheumatism, affections of the defeat. Sometimes in cases complicated osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be the exception of the syringomyelia. In some cases, to the impossibility of the realization of the magnetic resonance imaging shows the myelography.
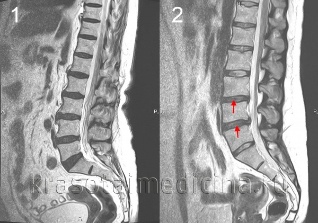
Aim the study affected intervertebral disc is made possible with the help of the discography. Electrophysiological studies are used to determine the degree and location of the lesion of the nerve pathways, to monitor the recovery process in the course of the therapy.
The treatment of the osteochondrosis of the spine
In the period of acute shows the peace in the affected spinal motor segment. To this end, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine apply fixing to the neck of the pit, to the osteochondrosis lumbar — rest in bed. The fastening is necessary and to the osteochondrosis of cervical instability and vertebral segment.
In the medication therapy of osteochondrosis use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids): diclofenac, nimesulide, lornoxicam, meloxicam. With the intense syndrome painful shows pain medications, for example, an analgesic central action flupirtine. For the relief of muscle tension, use of muscle relaxants — tolperison, tizanidine. In some cases it is convenient to the appointment of anticonvulsants - carbamazepine, gabapentin; antidepressants, among which a preference for the reuptake inhibitors of serotonin (sertraline, paroxetine).
When there is radicular syndrome of the patient is shown the hospital treatment. Local the introduction of glucocorticoids, the therapy against oedema, the application of traction. In the treatment of degenerative disc disease, it is widely used in physiotherapy, reflexology, massage, therapeutic exercise. The application of manipulative therapy requires the compliance of the technique of their execution and a special care in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Surgery of the spine is shown to all, with a significant compression of the spinal cord. Involves the removal of the herniation of the intervertebral disk and the decompression spinnomozgovogo of the channel. It is possible to carry microdiscectomy, laser, reconstruction of the unit, the replacement of the affected unit, the implant-stabilizing the vertebral segment.












































